An essay definition can be described as a focused piece of writing intended to inform or persuade within the context of academic writing. The essay purpose surrounds with clear writing goals, whether for informational writing, persuasive writing, or creative expression.
Many students cannot write academic essays properly because they consider essays like casual writing, but understanding their formal role provides clarity and direction.
Key points about an essay include
–An essay is a focused piece of writing with a clear purpose.
-It is used to inform or persuade readers effectively.
-Essays serve academic writing goals in schools and universities.
-Essays fall into four main categories: argumentative essays, expository essays, narrative essays, and descriptive essays.
In university level writing, knowing the types of essays and having an overview of essay types helps students choose the right approach, structure, and style, improving clarity and academic performance.
Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay is centered around presenting an evidence-based argument with a thesis statement that reflects a clear stance. The goal is convincing the reader by combining research skills, quotations, and analysis.
A common challenge is relying on personal opinions without objective support, but using credible academic sources and proper citation or referencing ensures the argument is trustworthy.
In college-level writing, argumentation follows a structured format: an introduction to present the topic and thesis statement, body paragraphs to develop arguments and provide evidence, and a conclusion that summarizes the argument and emphasizes its importance.
Writers often struggle to balance different viewpoints, so encouraging critical thinking and thorough research strengthens the essay’s persuasiveness.
Argumentative Essay Structure Example
| Section | Purpose | Key Elements |
| Introduction | Present topic and thesis | Thesis statement, background information, clear stance |
| Body Paragraphs | Develop argument | Quotations, analysis, objective support, research findings |
| Conclusion | Wrap up essay | Summarize argument, emphasize importance, reinforce thesis |
| Research & Citation | Ensure credibility | Academic sources, proper citation and referencing |
| Critical Thinking | Strengthen persuasiveness | Weigh counterarguments, form contentious claim |
Expository Essays
An expository essay provides a focused explanation of a topic, offering a balanced view in a well-organized structure. Its aim is to demonstrate topic knowledge while ensuring clear communication through factual information and an objective tone. A common challenge is adding personal opinions, which can compromise clarity; maintaining focus on facts and evidence ensures the essay remains informative.
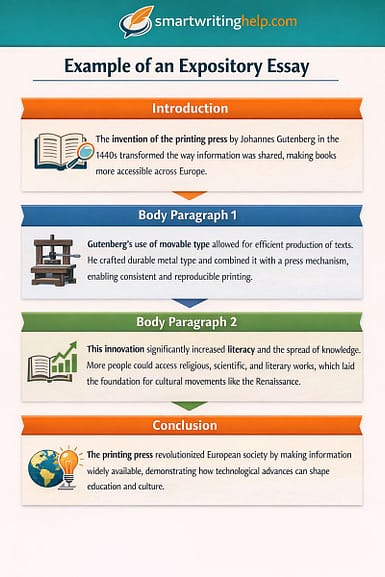
In high school assignments and college exams, an expository essay typically follows a structured format with an introduction presenting the topic and background information, body paragraphs offering a detailed explanation of processes or ideas, and a conclusion summarizing information.
Writers often struggle with logical organization, so planning sections before writing helps maintain clarity and conciseness.
Steps of an Expository Essay Approach
- Introduction: Introduce the topic and provide background information.
- Body Paragraph 1: Explain the first process or idea with factual information.
- Body Paragraph 2: Present a second aspect or example with logical organization.
- Conclusion: Summarize information clearly and restate the main points without personal opinion.
Narrative Essay
A narrative essay centers on storytelling, often drawing from a personal experience or imaginative exploration. Its purpose is to create an engaging narrative using creative writing and a distinct personal voice.
A common challenge is maintaining clarity while being personal; balancing vivid descriptions with a clear structure ensures readers follow the story without losing interest.
These essays have a flexible structure but usually start with a beginning setup, develop the story with meaningful events, and conclude with a meaningful ending that highlights life lessons or insights.
Writers often use reflection to convey the point of the story, turning experiences into learning experiences that illustrate personal growth.
Example of a Narrative Essay Approach
- Beginning Setup: Describe initial circumstances and context, introducing the narrator’s situation.
- Story Development: Narrate key events with rich details, showing challenges and turning points.
- Reflection: Highlight lessons learned and moments of self-discovery.
- Meaningful Ending: Conclude by connecting the experience to broader insights or personal growth.
Descriptive Essays
A descriptive essay is a type of writing that captures a focused subject in detail, allowing the reader to experience it through sensory description and sensory language. These essays rely on figurative language, creative expression, and careful word choice to create memorable imagery and convey the emotional tone of the scene. Key features include:
- Highlighting place description or object description
- Using observation to enhance originality
- Conveying atmosphere and overall mood
- Maintaining a loosely structured format with an introduction of the subject and an overall impression
Example
During late-night study hours, a lamp lights up scattered notes and open books. The quiet environment and organized materials make it easier for the student to concentrate and revise efficiently.
Understanding Textual Analysis Essays
A textual analysis essay requires close reading and careful reading of academic texts to provide a critical interpretation. These essays test your analytical skills by explaining effects, using evidence from the text, and offering thoughtful interpretation.
The goal is to focus on literary and rhetorical study, examining how the text communicates meaning rather than simply summarizing it.
Example – Student-Related Text Analysis
In her essay, the professor uses repetition to emphasize the importance of time management. A line stating, “Deadlines are the heartbeat of learning,” illustrates the analysis focus on structure.
Through quotations and careful close reading, it becomes clear that the repeated phrase underscores urgency and responsibility. This textual analysis essay demonstrates interpretation of both content and style, showing how small textual choices affect the reader’s understanding.
Key Parts:
- Introduction: Focus on repetition and time management
- Sensory/Analytical detail: “Deadlines are the heartbeat of learning”
- Observation/Analysis: Repetition emphasizes urgency and responsibility
- Evidence from text: Direct quotation
- Conclusion/Interpretation: Shows how the text conveys meaning and style
Rhetorical Analysis
A rhetorical analysis examines a persuasive text to evaluate the effectiveness of rhetorical devices. It requires analyzing the author’s construction, argument structure, and how ethos, pathos, and logos are used.
This essay type focuses on ethical appeal, emotional appeal, tone analysis, and the audience impact, connecting insights to broader relevance in speech analysis or political texts.
Example – Student-Friendly Rhetorical Analysis
| Part | Example in Text | Explanation |
| Introduction of Subject | In her campus speech, the student leader argues for better mental health support on campus. | Introduces the persuasive text and the argument structure. |
| Rhetorical Devices / Close Observation | She repeats the phrase “No student should struggle alone” to appeal emotionally. | Highlights rhetorical devices like repetition and emotional appeal (pathos). |
| Evidence / Quotations | “No student should struggle alone” | Uses a quotation as evidence from text to support the analysis. |
| Analysis / Effectiveness Evaluation | The repetition emphasizes solidarity and community, increasing the speech’s impact on students. | Shows effectiveness evaluation and audience impact. |
| Figurative / Prophetic Language | Her statement, “We will rise together,” conveys hope and calls for collective action. | Uses prophetic language and tone analysis to highlight persuasive effect. |
| Conclusion / Broader Relevance | The speech demonstrates how ethos, pathos, and logos work together to inspire action and awareness about mental health. | Connects the rhetorical analysis to broader relevance in student life. |
Literary Analysis
A literary analysis essay involves close reading of a literary work to explore themes, characters, setting, and the use of figurative language. It focuses on interpretation of the author’s choices, supported with textual evidence and quotations, forming an analytical argument for in-depth study of novels or poems.
Example – Student-Friendly Literary Analysis
| Part | Example | Explanation |
| Introduction of Subject | In To Kill a Mockingbird, Harper Lee explores themes of justice and empathy through Scout’s experiences. | Introduces the literary work and main themes. |
| Close Reading / Observation | Scout observes the trial of Tom Robinson, noticing how townspeople react to the events. | Shows narrative perspective and characters’ development. |
| Textual Evidence / Quotations | Atticus says, “You never really understand a person until you consider things from his point of view.” | Uses a quotation as textual evidence to support interpretation. |
| Analysis / Author’s Choices | Lee uses Scout’s innocent perspective to highlight prejudice and fairness, making the themes more impactful. | Discusses author’s choices and the effect on themes. |
| Figurative Language / Setting | The description of Maycomb as a “tired old town” conveys the social stagnation and entrenched bias. | Highlights figurative language and setting contributing to theme. |
| Conclusion / Interpretation | The novel’s events and Scout’s observations encourage readers to reflect on justice, morality, and empathy. | Summarizes analytical argument and interpretation. |
Choosing Right Essay Type as per Requirement
Selecting the appropriate essay type begins with carefully analyzing essay prompts. Look for keywords such as explain, describe, argue, or assess, which indicate the essay approach and writing purpose.
Understanding the assignment requirements and the academic context helps you interpret the prompt correctly and focus on the topic in a way that meets expectations. Instructional verbs in prompts are especially helpful for guiding your structure and style.
Differences of Essay Types
Understanding the differences between essay types helps students choose the right approach for each assignment. Argumentative vs expository essays both involve academic conventions and objective writing, but while argumentative essays require research-based writing to support a stance, expository essays aim to explain or inform without taking a side.
Similarly, narrative vs descriptive essays are more creative writing: narratives focus on storytelling and events, often using a personal tone, whereas descriptive essays emphasize descriptive intensity, using sensory details and figurative language to create vivid imagery.
Comparison of Essay Types
| Essay Type | Writing Focus | Key Features | Student-Friendly Example |
| Descriptive | Sensory description, vivid imagery | Focus on place/object, creative expression, emotional tone, figurative language, observation | Describe the campus library: sunlight on notebooks, sound of typing, smell of coffee, creating a memorable atmosphere. |
| Narrative | Storytelling, personal or imaginative | Focus on personal experience, story structure, personal tone, plot/events | Recount a first day at university: feeling nervous, meeting classmates, discovering favorite study spots. |
| Expository | Explain or inform | Objective writing, organized facts, no personal opinion, academic conventions | Explain how study schedules improve learning efficiency: steps, benefits, supporting details. |
| Argumentative | Take a stance and support it | Research-based writing, evidence, objective writing, persuasive structure | Argue whether school start times should be later: use studies and expert opinions to support position. |
| Textual Analysis | Analyze a text | Close reading, critical interpretation, textual evidence, quotations, analytical skills | Analyze a professor’s essay: repetition of key phrases emphasizes urgency and responsibility. |
| Rhetorical Analysis | Evaluate persuasive techniques | Rhetorical devices, ethos/pathos/logos, audience impact, tone analysis, broader relevance | Analyze a student leader’s speech: repetition and prophetic phrases encourage solidarity and action. |
| Literary Analysis | Interpret literary works | Themes, characters, setting, figurative language, narrative perspective, author’s choices | Analyze To Kill a Mockingbird: Scout’s perspective shows prejudice and fairness; quote and interpret key lines. |
Conclusion
Academic writing is essential for college essays, university assignments, and composition classes. It emphasizes independent research, forming an original argument, and maintaining academic standards. Effective academic essay relies on evidence-based writing, a formal tone, and structured essays to contribute to scholarly discussion.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know what type of essay to write?
Look at your essay prompts and focus on keywords like explain, describe, argue, or assess. These instructional verbs guide your essay approach and writing purpose. Understanding the assignment requirements and academic context helps you interpret the prompt correctly.
What type of essay is most common at university?
Argumentative essays are the most frequent in college essays and university assignments. They require research-based writing, forming an original argument, and following academic standards in a structured essay format.
What are the different types of academic essays?
The main types of academic essays include descriptive, narrative, expository, and argumentative essays. Analytical essays, such as literary, textual, and rhetorical analysis, are also common in academic writing.
What’s the difference between an expository essay and an argumentative essay?
An expository essay focuses on explaining a topic clearly, relying on objective writing without taking a side. An argumentative essay involves research-based writing to support a stance, using evidence from text or studies to build a persuasive analytical argument. The main difference is writing purpose: informing versus convincing.
What’s the difference between a narrative essay and a descriptive essay?
A narrative essay emphasizes storytelling focus and often uses a personal tone to convey experiences. A descriptive essay highlights descriptive intensity, sensory language, and figurative language to create memorable imagery of a place or object.





